Production of bioactive peptides during soybean fermentation and their potential health benefits
11 Jan 2024 . 10:35
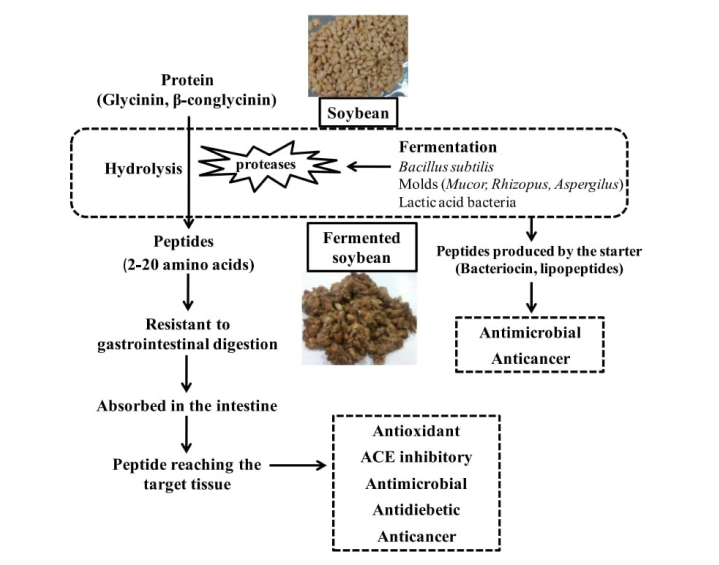
Background: Fermented soybean products are consumed in many Asian countries and are one of the potential sources of bioactive peptides. Soybean is fermented using bacteria (Bacillus subtilis and lactic acid bacteria) and fungi (Mucor spp., Aspergillus spp. and Rhizopus spp.), resulting in different types of fermented products. Scope and approach: This review article is focused on production of bioactive peptides in fermented soybean products and their role in prevention and treatment of several metabolic diseases. Studies on novel bioactive peptides having specific health benefits can lead to their application in the development of functional foods and pharmaceuticals with the aim replace synthetic drugs that have several side effects. Key findings and conclusions: Peptides in fermented soybean products are either released by the hydrolysis of soybean proteins during fermentation or produced by the microorganisms associated with fermentation. During soybean fermentation specific bioactive peptides are produced as a result of hydrolysis of soybean proteins (Glycinin and b-conglycinin). Individual microbial strains contribute in the formation of specific bioactive peptides with respective health benefits depending on the sequence and composition of amino acids. Such bioactive peptides may act like regulatory compounds and exhibit bioactive properties such as anti-hypertensive, antimicrobial, antioxidant, anti-diabetic and anticancer activities. Studies in future, on application of specific strains for soybean fermentation can lead in to the formation of novel bioactive peptides with potential health benefits.
Artikel Lainnya
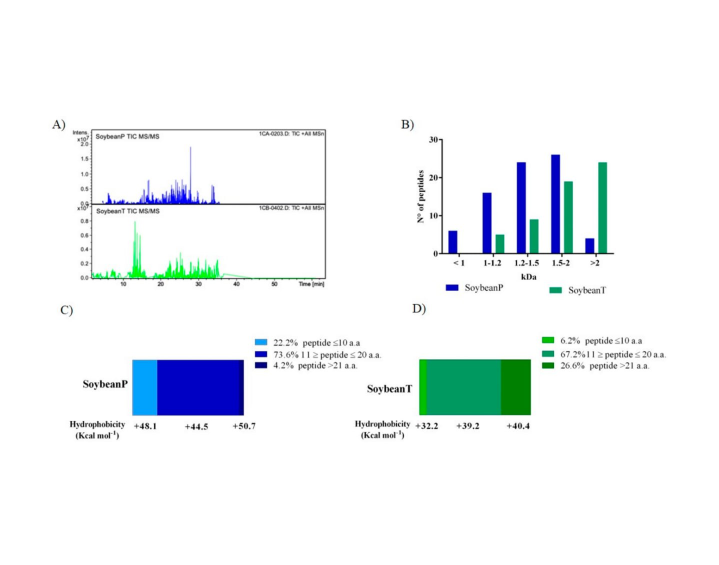
Soybean Peptides Exert Multifunctional Bioactivity Modulating 3Hydroxy-3-Methylglutaryl-CoA Reductase and Dipeptidyl Peptidase-IV Targets in Vitro
This study was aimed at evaluating the cellular mechanism through which peptic (P) and tryptic (T) soybean hydrolysates modulate the targets ...
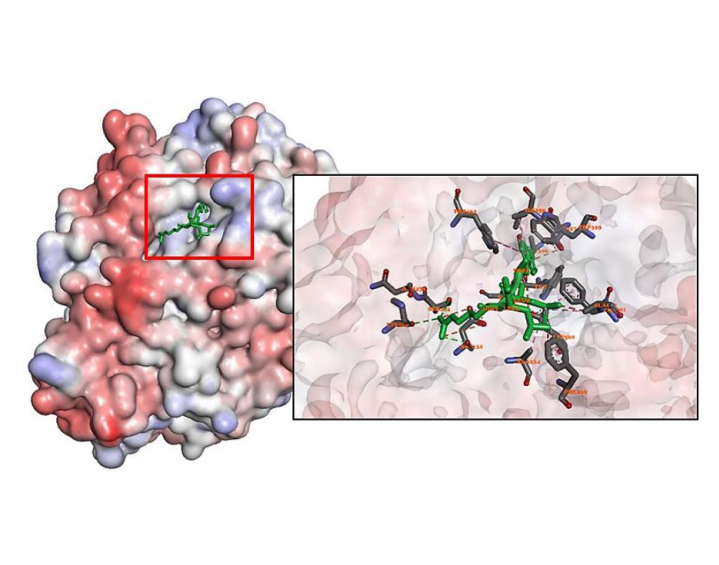
Identifikasi Peptida Bioaktif dari Protein Kedelai sebagai Inhibitor Enzim -glukosidase untuk Kandidat Antidiabetes
Diabetes mellitus merupakan salah satu gangguan metabolisme endokrin yang telah menyebabkan morbiditas dan mortalitas di seluruh dunia. Diper...