Soybean Peptides Exert Multifunctional Bioactivity Modulating 3Hydroxy-3-Methylglutaryl-CoA Reductase and Dipeptidyl Peptidase-IV Targets in Vitro
11 Jan 2024 . 10:34
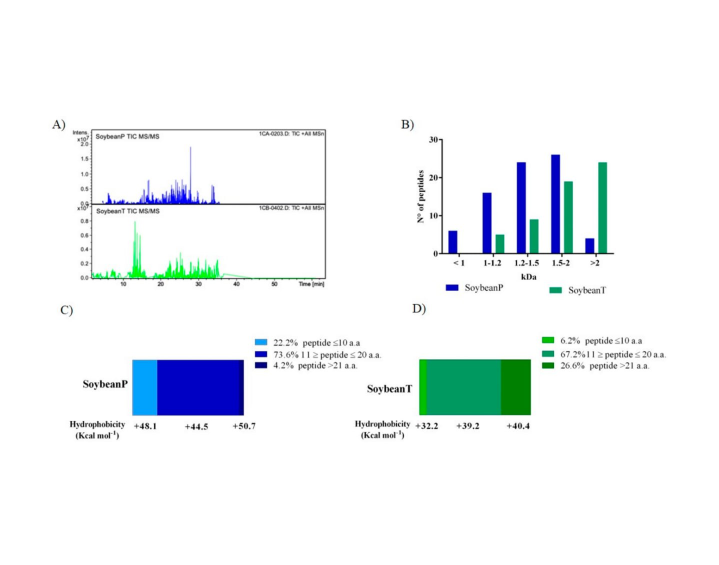
This study was aimed at evaluating the cellular mechanism through which peptic (P) and tryptic (T) soybean hydrolysates modulate the targets involved in hypocholesterolemic pathways in HepG2 and antidiabetic pathways in Caco-2 cells. Both hydrolysates (tested in the concentration range of 0.5−2.5 mg/mL) inhibited the 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl-CoA reductase activity in HepG2 cells. In addition, Soybean P increased LDLR protein levels on HepG2 membranes by 51.5 ± 11.6% and 63.0 ± 6.9% (0.5−1.0 mg/mL) whereas Soybean T increased them by 55.2 ± 9.7% and 85.8 ± 21.5% (0.5−1.0 mg/ mL) vs the control, with a final improved HepG2 capacity in the uptake of extracellular LDL. Soybean P reduced in vitro the dipeptidyl peptidase-IV activity by 16.3 ± 3.0% and 31.4 ± 0.12% (1.0 and 2.5 mg/mL), whereas Soybean T reduced it by 15.3 ± 11.0% and 11.0 ± 0.30% (1.0 and 2.5 mg/mL) vs the control. Finally, both hydrolysates inhibited dipeptidyl peptidase-IV activity in situ in human intestinal Caco-2 cells. This investigation may help to explain the activities observed in experimental and clinical studies
Artikel Lainnya
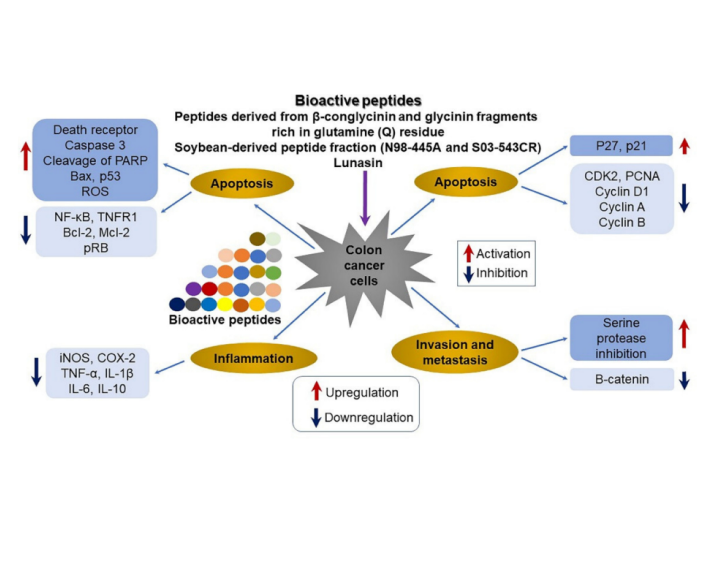
Beneficial Effects of Soybean-Derived Bioactive Peptides
Peptides present in foods are involved in nutritional functions by supplying amino acids; sensory functions related to taste or solubility, e...
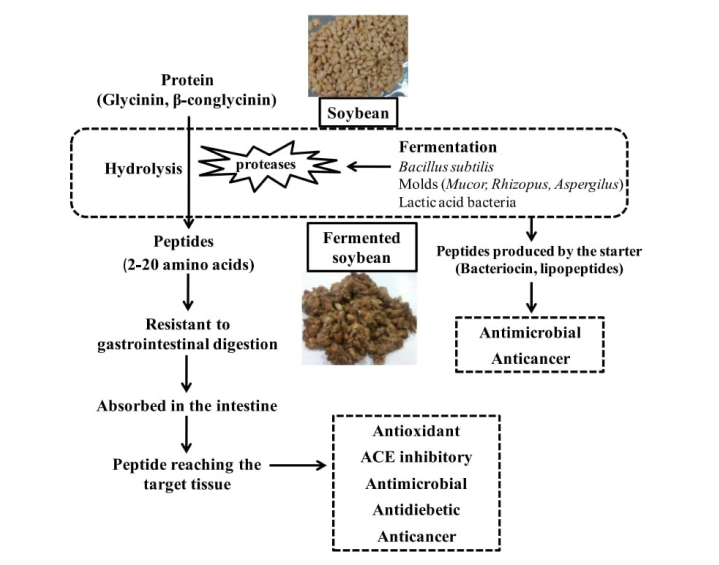
Production of bioactive peptides during soybean fermentation and their potential health benefits
Background: Fermented soybean products are consumed in many Asian countries and are one of the potential sources of bioactive peptides. Soybe...