Discovery of potential small molecular SARS-CoV-2 entry blockers targeting the spike protein
08 Jan 2024 . 16:32
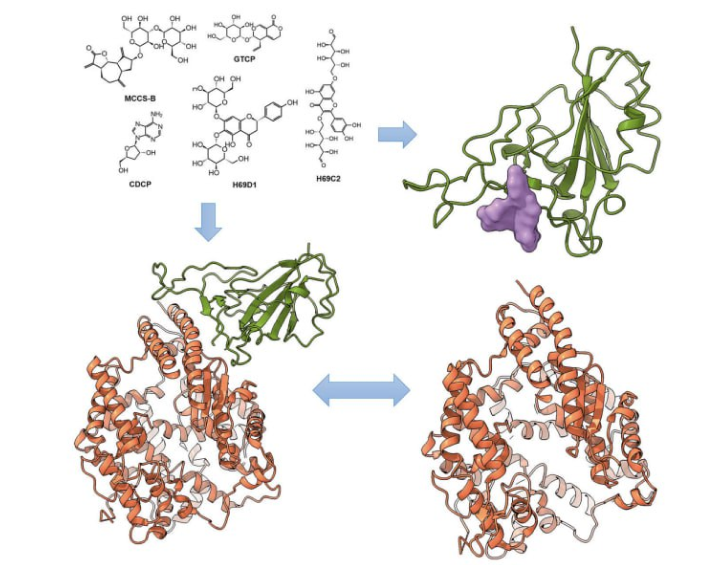
An epidemic of pneumonia caused by severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) is spreading worldwide. SARSCoV-2 relies on its spike protein to invade host cells by interacting with the human receptor protein Angiotensin-Converting Enzymes 2 (ACE2). Therefore, designing an antibody or small-molecular entry blockers is of great significance for virus prevention and treatment. This study identified five potential small molecular anti-virus blockers via targeting SARS-CoV-2 spike protein by combining in silico technologies with in vitro experimental methods. The five molecules were natural products that binding to the RBD domain of SARS-CoV-2 was qualitatively and quantitively validated by both native Mass Spectrometry (MS) and Surface Plasmon Resonance (SPR). Anti-viral activity assays showed that the optimal molecule, H69C2, had a strong binding affinity (dissociation constant KD) of 0.0947 µM and anti-virus IC50 of 85.75 µM.
Artikel Lainnya
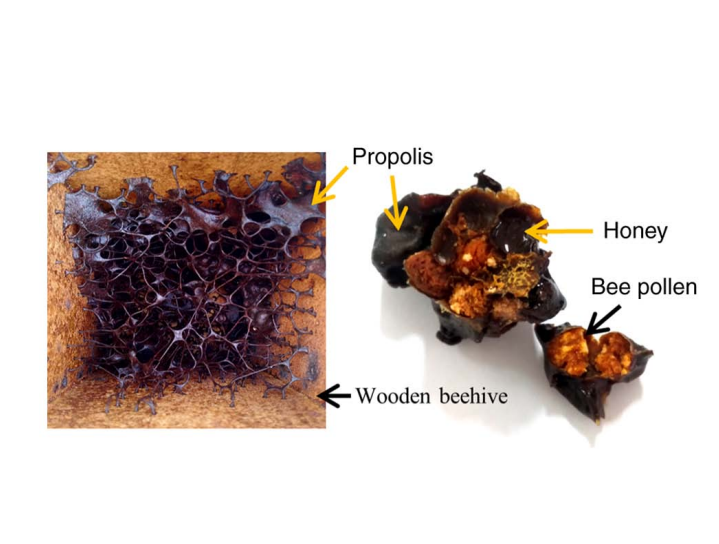

Water soluble propolis and bee pollen of Trigona spp. from South Sulawesi Indonesia induce apoptosis in the human breast cancer MCF7 cell line.
Bee products are best known as one of the beneficial natural products providing multiple pharmacological effects, such as antimicrobial, anti...
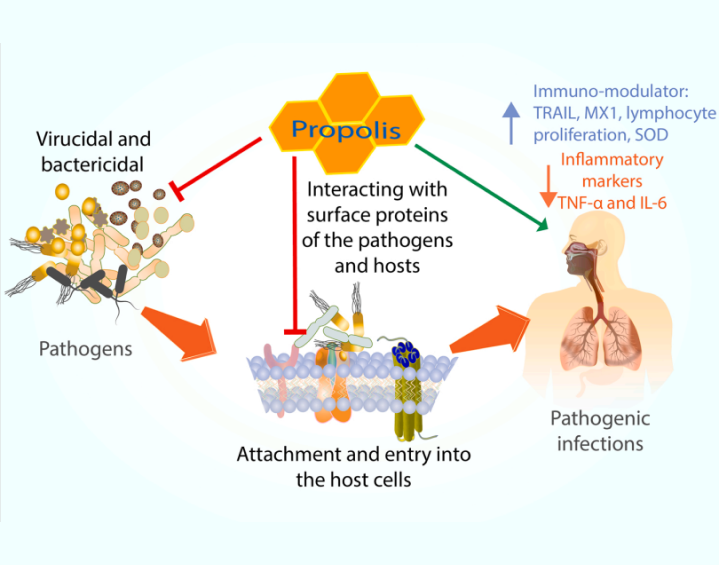
The Potential Use of Propolis as a Primary or an Adjunctive Therapy in Respiratory Tract-Related Diseases and Disorders A Systematic Scoping Review
Propolis is a resinous beehive product that is collected by the bees from plant resin and exudates, to protect and maintain hive homeostasis....